

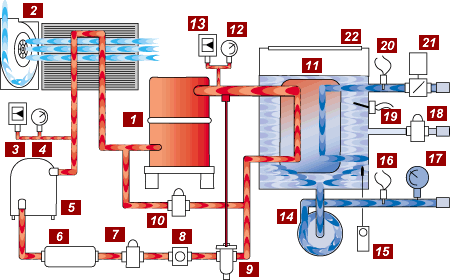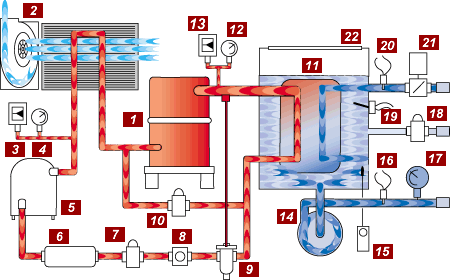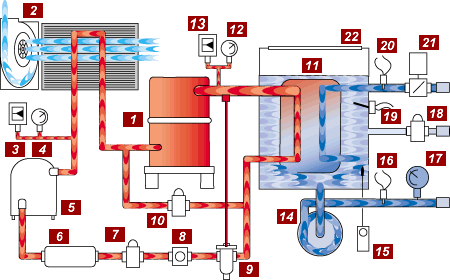
Compressor (#1)
The compressor has two functions in the refrigerant cycle. First, it removes the refrigerant vapor from the evaporator and reduces the pressure in the evaporator to a point where the desired evaporating temperature can be maintained. Second, the compressor raises the pressure of the refrigerant vapor to a level high enough so that the temperature is higher than the temperature of the cooling medium available for condensing in the refrigerant vapor.
Air-Cooled Condenser (#2)
The air-cooled condenser is a heat exchanger where the process heat absorbed by the refrigerant is given off to the air around it. As heat is given off by the high temperature high pressure vapor, its temperature falls until the vapor condenses to a liquid. A centrifugal blower or motor driven fans generate airflow across the condenser.
High Pressure Limit (#3)
Protects the system against excessive pressure in the refrigerant circuit.
High Pressure Pressure Gauge (#4)
Provides visual indication of the refrigerant condensing pressure.
Liquid Receiver (#5)
The receiver is required to hold the system refrigerant charge during service.
Filter Drier (#6)
The Filter Drier removes moisture, dirt, and other foreign materials from the refrigerant that will harm the system components and reduce efficiency.
Liquid Line Solenoid (#7)
The Liquid Line Solenoid is an electrically controlled refrigerant flow control valve that closes when the compressor stops. This prevents liquid refrigerant from migrating to the evaporator and causing liquid slugging when the compressor starts again. Liquid slugging can cause severe damage to the compressor. The valve is opened when the compressor is on.
Refrigerant Sight Glass (#8)
The Refrigerant Sight Glas allows the operator or serviceman to observe the flow of liquid refrigerant. Adequate refrigerant is determined by a clear liquid flow. Bubbles in the liquid flow indicate a shortage of refrigerant. The moisture indicator provides a warning in the event that moisture enters the system, indicating that service is required. A green indicator signals no moisture content. A yellow indicator signals that the system is contaminated with moisture and requires service.<
Expansion Valve (#9)
The Expansion Valve meters the flow of liquid refrigerant into the evaporator at the proper rate to provide cooling of the process water. As more cooling is required, additional refrigerant is metered through the valve into the evaporator.
Hot Gas Bypass Valve (#10)
The Hot Gas Bypass Valve (not included with Digital Scroll Compressors) prevents short cycling of the compressor by modulating the compressor capacity. When activated, the valve opens and allows hot refrigerant gas to enter the refrigerant stream entering the evaporator. This reduces the effective capacity of the system. Units using Digital Scroll Compressors unload internally using energy saving separation of the compressor scroll plates.
Evaporator (#11)
The EVAPORATOR is the device in which liquid refrigerant boils, absorbing heat as it evaporates, cooling the process fluid.
Low Pressure Refrigerant Gauge (#12)
Provides visual indication of the refrigerant evaporating pressure.
Low Refrigerant Pressure Limit (#13)
Protects the system against low pressure in the refrigerant circuit.
Coolant Pump (#14)
The Coolant Pump circulates chilled fluid through the process loop.
Freezestat Limit (#15)
The FREEZESTAT aids in protecting the evaporator from potential freezing. This is an option on most models.
To Process Sensor Probe (#16)
The To Process Sensor Probe is placed in the coolant flow stream going to the process. Control decisions are made based on the To Process coolant temperature.
Coolant Pressure Gauge (#17)
Provides visual indication of the coolant pressure supplied to the process.
Water Make-Up Solenoid (#18)
When activated by the float switch, the WATER MAKE UP SOLENOID will open and introduce supply water to the reservoir. This restores the reservoir to the proper operating level.
Reservoir Level Float Switch (#19)
The Reservoir Level Float Switch is place at the proper water level in the reservoir. If the water level falls below the proper level, the float switch activates the Water Make-Up Solenoid valve refilling the tank to the proper level.
From Process Sensor Probe (#20)
The From Process Sensor Probe is placed in the coolant flow stream coming back from the process. Note: this is an option available on LE & HE control instruments only.
Evaporator Flow Switch (#21)
The Evaporator Flow Switch protects the system from low coolant flow conditions that can cause system operating problems and damage. Note: This is an option on most models.
Reservoir (#22)
The Coolant Reservoir is selected to have adequate volume to support the flow requirements of the chiller. The reservoir is non-pressurized promoting air separation and high process flows.
Need Application Assistance?
Our Experienced Team Can Save You Time & Money.
Tell Us About Your Project